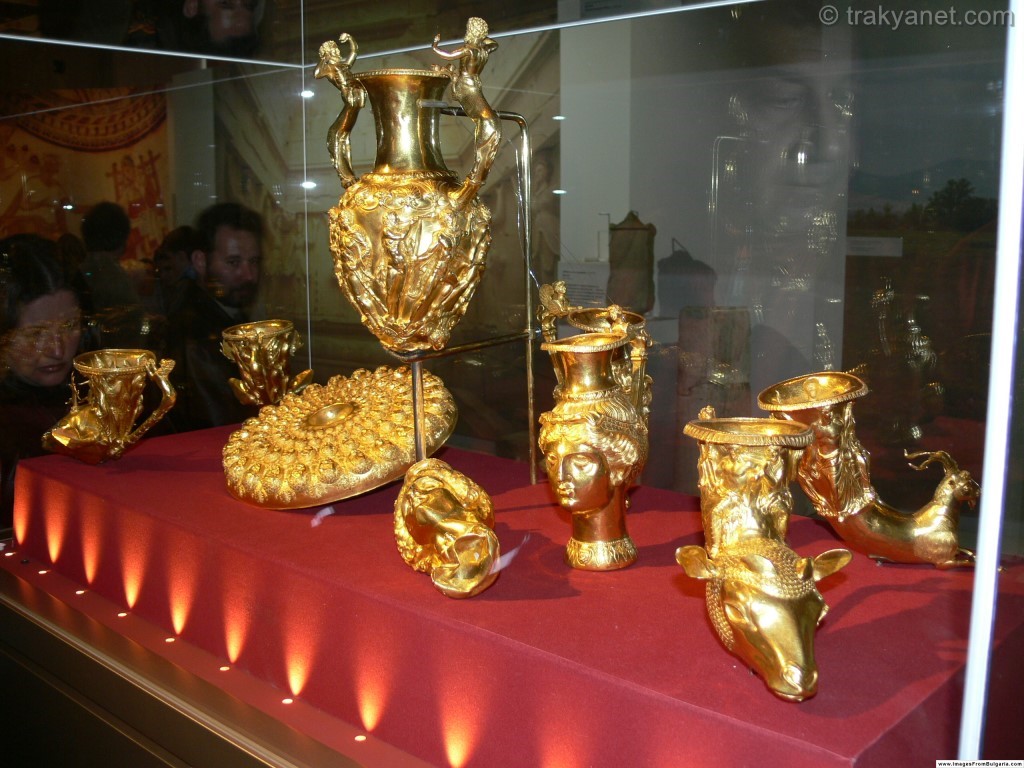
Thrace is probably one of the last regions that comes to mind when it comes to cultural tourism focused on antiquities in our country. Aside from Ottoman structures and tumuli in a few Thracian cities, there's a common misconception that Thrace is devoid of antiquities. However, we all know that Thrace is the easiest passage between Europe and Asia and, due to its strategic geographical location, holds great cultural historical significance.
There are several reasons for the lack of interest in Thracian archaeology; foremost among these is the fact that the archaeological remains in Thrace are very different from those we are accustomed to in Anatolia. Large mounds and archaeological sites are, if not absent, very few in number in Thrace, as they are in Anatolia. However, this is not due to the poverty of Thracian archaeology, but rather to the fact that it underwent a very different developmental process in its cultural history than in Anatolia. Due to the natural environmental conditions, adobe and stone were used in Anatolian architecture, while wood was used in Thrace, which influenced the appearance of the remains. A second reason for this lack of interest is that archaeology in Turkey has developed largely through a "Mesopotamian" focus and has not shown much interest in European archaeology. Consequently, Turkish archaeological interest has been focused outside Thrace; this, coupled with the long closure of Thrace to archaeological research for military reasons, has meant that Thrace remained an "unknown region" until recently.
Despite this lack of interest, Thrace holds strategic intercontinental importance due to its geographical location, and solutions to many questions concerning cultural history must be sought in this region. This region lies, on the one hand, at the junction of Southeastern Europe and the Anatolian peninsula, and, on the other, at the narrow strait of the sea route between the Black Sea and the Aegean-Mediterranean cultures. Therefore, problems related to all kinds of intercontinental relations, such as migration, invasion, cultural exchange, or interaction, can only be resolved through research in Thrace. Similarly, the resolution of the problems between the Anatolian, European, and Aegean chronological systems depends on data obtained from Thrace. Furthermore, questions regarding the origins of European civilization and the extent to which Anatolian and Near Eastern civilizations influenced its development can only be understood through archaeological research in Thrace.